Removing All of or a Portion of Your Nail to Treat Nail Fungus – Is it Effective?
Removing All of or a Portion of Your Nail
to Treat Nail Fungus – Is it Effective?
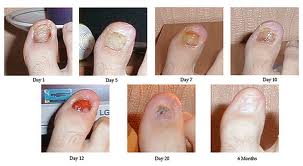 No one really knows. Little to no research has been done on removing all or part of the nail to treat a nail fungus infection. That’s because it’s sort of a last resort treatment for dealing with onychomycosis. However if you are unable to take any of the oral medications suggested for treating onychomycosis and if none of the topical solutions are effective, or if you have tried treating your nail fungus in several ways and none of them have been effective, then surgery may be an option.
No one really knows. Little to no research has been done on removing all or part of the nail to treat a nail fungus infection. That’s because it’s sort of a last resort treatment for dealing with onychomycosis. However if you are unable to take any of the oral medications suggested for treating onychomycosis and if none of the topical solutions are effective, or if you have tried treating your nail fungus in several ways and none of them have been effective, then surgery may be an option.
Another thing to consider is if you continue to experience recurring nail fungus infections, you might need to make some dietary changes and/or do a medical cleanse to get the possible sources of infection out of your system.
How does it work?
Your options for having your nail removed are as follows:
- Complete removal – known as avulsion
- Partial removal – known as debridement
There are also two options for having these procedures done:
- Surgery – Your doctor will numb the skin around and under your nail with a local anesthetic, either topical or a shot. Then a tool will be used to separate your nail from the surrounding skin and nail bed. (Your nail bed is the skin underneath your nail. This is most commonly where a nail fungus hides and breeds.) Once the nail has been removed your nail bed and surrounding skin should heal in 2-3 weeks.
- Ointment – Your doctor will cover the skin around your infected nail to protect it (similar to taping a window or door while painting.) Then an ointment will be put on the infected nail. The infected nail is covered with a plastic dressing, which will need to be kept dry. After a week to a week and a half, your nail should be soft enough to be removed by your doctor. The exposed nail bed and surrounding skin should heal in 2-3 weeks.
After you have undergone either of these procedures, your doctor will probably recommend taking an oral antifungal medication, or putting a topical ointment on the exposed nail bed to deliver the medicine directly to the affected area.
A fingernail, once the infected portion is removed should grow back healthy within about 6 months. A toenail may take up to 18 months to grow back.
If infection continues after this procedure, your doctor may recommend completely removing the nail again and putting a chemical on the cuticle (the soft layer of skin at the base of your nail) to prevent your nail from growing back.
Does it help?
Again, no one really knows as no one has put the time and research into the effects of removing part or all of the nail to cure onychomycosis.
So far, there is one reliable study that compared taking oral antifungal medication against other types of treatment, including removing part of the nail and putting a topical antifungal medication directly on the nail bed. The results were that people who chose the oral antifungal medication were happier with their treatment outcome than people who had part of their nail removed or who used any sort of topical remedy.
Possible Side Effects?
Once your nail has been removed from the nail bed, you will need to keep it clean and dry to prevent possible further infection of the area. Your doctor may also recommend using an antibiotic cream to ensure that everything heals well and stays healthy.
Another possible problem is that the side or corner of your nail could re-grow into the skin surrounding your toe. This is referred to as an ingrown toe nail. Mild symptoms of an ingrown toenail can be treated by soaking your foot in warm salt water and then propping the ingrown porting of your toenail to encourage it to grow above the skin. A more severe ingrown toenail will require you to return to your doctor for treatment.