What are the symptoms of a Nail fungus and how can I tell if I have a Nail Fungus Infection?
What are the symptoms of a Nail fungus and
how can I tell if I have a Nail Fungus Infection?
 You’d think these would be fairly straightforward questions that ought to illicit simple answers. Unfortunately not only is this not true, but it is confusing enough that sometimes doctors misdiagnose nail fungus (or onychomycosis). Knowing the symptoms will assist you in helping your doctor to order the appropriate diagnostic tests so that you end up with the correct solution to your problem.
You’d think these would be fairly straightforward questions that ought to illicit simple answers. Unfortunately not only is this not true, but it is confusing enough that sometimes doctors misdiagnose nail fungus (or onychomycosis). Knowing the symptoms will assist you in helping your doctor to order the appropriate diagnostic tests so that you end up with the correct solution to your problem.
There are two basic causes of nail infections. Bacterial and fungal. Onychomiycosis, or fungal nail infection, is usually caused by a dermatophyte called Trichophyton rubrum. If not, it is caused by Candida albicans, a yeast growth (also a fungus). As nail infections differ in variety and in cause, the correct cure must be applied. A fungal infection should be treated with an anti-fungal whereas a bacterial infection should be treated with an antibiotic.
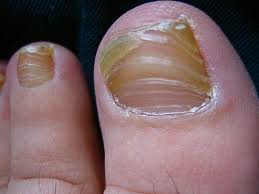
Onychomycosis affects the nail bed (skin underneath the nail) nail plate (the hard surface that we refer to as the nail) or the skin around the nail. About one third of skin infections and half of nail infections are caused by Onychomycosis. The visual signs are the abnormalities caused by the nail fungus. A white or yellowish crust appears on top of or embedded in the nail. This is the actual fungus growth. Sometimes it appears as streaks that follow the line of the nail against the infected digit (finger or toe) and sometimes it appears at the cuticle (soft area at the base of the nail). As the fungus spreads, it covers the entire surface of the nail, turning it to a milky white or yellow. Frequently it causes the nail to become ridged and deformed. This is a result of the dermaptophytes emitting destructive waste product as a result of consuming keratin. If the fungus gets underneath the nail plate, it can cause the nail bed to become irregular. This causes the nail plate to release from the bumpy nail bed and the nail becomes loose and can fall off.
If the nail fungus infection becomes severe, or if it contains Candida, the area around the nail can become swollen and sensitive to the touch. The skin may express (think ooze) pus and be very uncomfortable, even painful. These are common signs of infection. The pus is a result of white blood cells rushing to the area to fight off the infection. This is your body trying to do its job and tell you and your doctor that something is wrong.
It is most common for pus to be present in the case of bacterial infections. Thus your doctor should check for this before looking for fungal infections. To add to the confusion, there are diseases that mimic a nail fungus, including hallopeau acrodermatitis, lichen planus, nail bed psoriasis (which can occur in conjunction with fungal infection of the nail), nail bed melanoma, Reiter syndrome, yellow nail syndrome, onycholysis, and paronychia. Because of this factor, more than one test may be necessary to determine the correct course of treatment.
Different forms of onychomycosis will require different samples from the affected area. In some cases the nail can be sampled from the end or the top can be scraped for a sample, in others, the nail will need to be removed entirely. Whereas this can be a bit scary, it is also to your advantage as it then exposes the nail bed so that it can be treated.
The most typical tests performed on a nail culture to look for onychomycosis are a potassium hydroxide wash, which allows for the sample to be put under a microscope and searched for evidence of fungal growth, or a fungal culture, where the sample piece of nail is put in an environment (usually a petri dish) where it has the necessary components to thrive and create new growth, thus showing what kind of fungal infection it is. In the unlikely event that neither of these tests show positive for onychomycosis, the remaining nail sample can be pulverized and sent to a pathology lab for analysis or submitted for a bacterial culture if it is determined that the infection is bacterial instead of fungal.
Determining what kind of infection you have and what to do about it are very important when dealing with a nail infection of any kind. Having the infected area looked at by a physician, preferably a dermatologist, is the best way to deal with these diseases as they can help to rule out and diagnose serious problems as well as knowing what to do about the infection in the first place.